The Hidden Impact of Brain Injuries
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a disruption in normal brain function caused by an external force, such as a blow to the head or an object penetrating the skull. These injuries range from mild concussions to severe, life-threatening conditions.
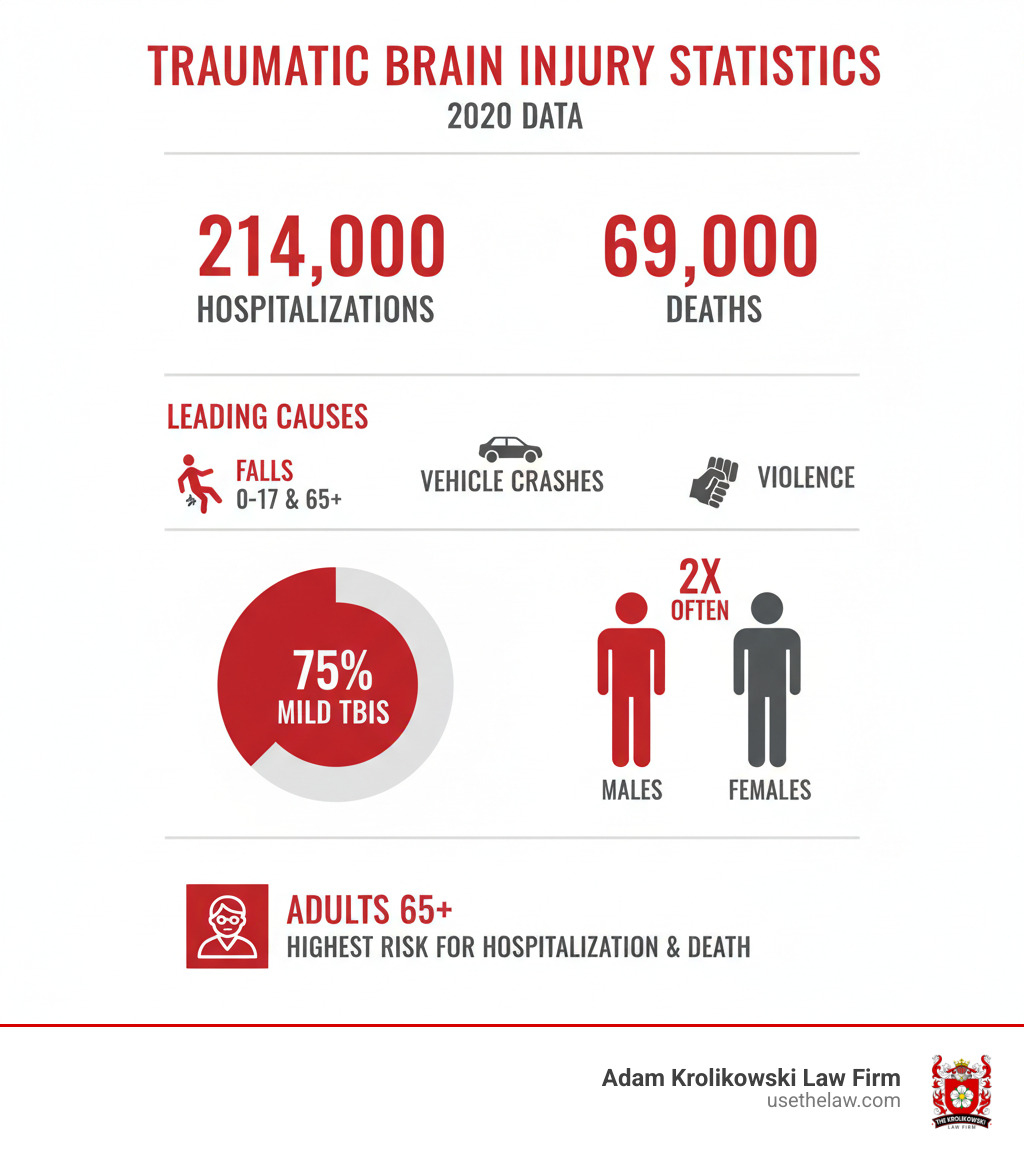
Common causes include falls, vehicle crashes, violence, and sports injuries. While anyone can be affected, males sustain TBIs more often than females, and adults over 65 face the highest risk of hospitalization and death. In 2020 alone, TBIs led to over 214,000 hospitalizations and 69,000 deaths in the U.S.
What makes TBI particularly challenging is its often “silent” nature. Over 75% of TBIs are considered mild, but even these can cause serious, long-lasting problems. Symptoms can be delayed, appearing hours, days, or even weeks after the initial injury, leading many to underestimate the severity.
A TBI can impact every aspect of a person’s life, affecting their work, relationships, and independence. If an injury was caused by someone else’s negligence, understanding the condition is the first step toward recovery and securing the compensation you deserve.
Terms related to traumatic brain injury:
- personal injury lawyer orange county
- santa ana bicycle accidents lawyer
- construction accident lawyer
Understanding Traumatic Brain Injury: Types and Causes
A traumatic brain injury unfolds in two stages. The primary injury is the immediate damage from the impact, such as bruising or bleeding. The secondary injury follows hours or days later, as a chain reaction of swelling, inflammation, and cell damage spreads through the brain. This delayed phase can significantly worsen the outcome, which is why prompt medical care is critical to manage and prevent further damage.
Certain groups face a higher risk. Falls are the leading cause of TBI for young children and adults over 65, with seniors having the highest rates of TBI-related hospitalization and death. Across all ages, males are affected about twice as often as females.
Classifying TBI: From Mild to Severe
Doctors classify traumatic brain injuries by severity to guide treatment and predict recovery.
- Mild TBI: Commonly known as a concussion, this accounts for over 75% of all brain injuries. A person may lose consciousness for a few seconds or minutes, or not at all, but feel confused. Symptoms include headaches, dizziness, and memory issues. Though called “mild,” these injuries require immediate medical attention.
- Moderate TBI: This involves a loss of consciousness from 20 minutes to several hours and post-traumatic amnesia (confusion) for up to 24 hours. Symptoms are more intense and last longer than in mild TBI.
- Severe TBI: This is characterized by a loss of consciousness for more than several hours or post-traumatic amnesia lasting over 24 hours. These injuries can cause permanent disability or death.
Medical professionals use the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) to assess severity shortly after an injury. It scores eye, verbal, and motor responses, with scores from 3 (deep coma) to 15 (fully awake). A score of 13-15 indicates a mild TBI, 9-12 suggests a moderate TBI, and 3-8 points to a severe TBI.
Common Causes of Head Trauma
- Falls: The leading cause of TBI, especially for young children and older adults.
- Vehicle-related collisions: Car, motorcycle, and bicycle accidents are a major cause of head trauma. The brain can slam against the skull from the force of impact, as seen in many brain injury car accident cases.
- Violence: Assaults, domestic violence, and gunshot wounds can cause severe brain damage. This includes child abuse, such as from scientific research on shaken baby syndrome. An attorney head injury can help steer the legal aspects of these situations.
- Sports injuries: Contact sports like football, hockey, and soccer carry a high risk of head impacts. A concussion injuries attorney can advise on your rights if you’ve been injured.
- Explosive blasts: These are a significant cause of TBI among military personnel, as the pressure waves can cause unique brain damage.
If your injury was due to someone else’s negligence, a head injury attorney can help you understand your options.
Recognizing the Signs and Diagnosing TBI
Symptoms of a traumatic brain injury can be subtle and may not appear for hours, days, or even weeks. This delayed onset makes TBIs dangerous, as people may not connect their symptoms to the initial injury. It is crucial to seek medical evaluation after any head injury, even if you feel fine, as early diagnosis is key to recovery.
Signs and Symptoms in Adults and Children
Symptoms of a traumatic brain injury vary based on injury severity and the individual.
In adults, watch for:
- Physical symptoms: Persistent headaches, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, dizziness, balance problems, slurred speech, and sensitivity to light or sound.
- Sensory symptoms: Blurred vision, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), a bad taste in the mouth, or changes in the sense of smell.
- Cognitive symptoms: Memory or concentration problems, confusion, mental fog, and slowed thinking.
- Emotional changes: Irritability, mood swings, anxiety, depression, and changes in sleep patterns.
In children, who may not be able to communicate their symptoms, look for:
- Changes in eating or nursing habits.
- Persistent irritability or fussiness.
- Unsteady walking or loss of balance.
- Loss of interest in favorite toys or activities.
- Changes in sleep patterns or seizures.
The Diagnostic Process for a Traumatic Brain Injury
Diagnosing a TBI involves several steps to understand the extent of the injury.
- Neurological Examination: A provider assesses mental status, motor and sensory function, reflexes, and coordination. The Glasgow Coma Scale is often used in acute settings to measure consciousness.
- Cognitive Testing: Neuropsychological tests evaluate memory, attention, and problem-solving skills, which can reveal damage not visible on scans.
- Imaging Tests: A CT scan is typically used first in emergencies to quickly detect bleeding, fractures, or swelling. An MRI provides a more detailed view of the brain tissue and can identify subtle damage that a CT scan might miss.
- Intracranial Pressure (ICP) Monitoring: For severe TBIs, a device may be surgically placed in the brain to monitor pressure, as liftd ICP can cause further damage.
Navigating a TBI diagnosis can be overwhelming. A traumatic brain injury lawyer can help you understand the medical and legal aspects of your case.
The Road to Recovery: Treatment, Rehabilitation, and Long-Term Effects
Recovery from a traumatic brain injury is a unique and personal journey. It requires a team approach and an individualized care plan, as the timeline can range from weeks for mild injuries to lifelong care for severe ones.

Immediate and Long-Term Treatment Strategies
Emergency care focuses on stabilizing the patient and minimizing secondary brain injury. This involves ensuring adequate oxygen and blood flow to the brain. For moderate to severe injuries, surgery may be needed to remove blood clots, repair skull fractures, or relieve pressure on the brain.
Medications are also critical. Diuretics like hypertonic saline can reduce brain swelling, while anti-seizure drugs prevent seizures. In some severe cases, coma-inducing drugs such as barbiturates may be used to reduce the brain’s metabolic demands. Other treatments being studied include tranexamic acid to control bleeding and simple interventions like elevation of the head to lower pressure.
The Crucial Role of Rehabilitation
Once a patient is stable, rehabilitation begins. A physiatrist often leads a team of specialists:
- Physical therapists work on strength, balance, and mobility.
- Occupational therapists help with daily living activities like dressing and eating.
- Speech and language pathologists address communication and swallowing issues.
- Neuropsychologists help manage cognitive, emotional, and behavioral changes.
Social workers, vocational counselors, and family members are also vital to the support system. Organizations like the Brain Injury Association of America provide valuable resources and support.
Potential Complications and Long-Term Effects of a Traumatic Brain Injury
A traumatic brain injury can have lasting effects. Common long-term challenges include:
- Cognitive deficits: Problems with memory, attention, and executive functions like planning and decision-making.
- Physical disabilities: Weakness, paralysis, spasticity (muscle stiffness), and balance problems.
- Seizures: These can develop long after the initial injury, leading to post-traumatic epilepsy.
- Emotional and behavioral changes: Irritability, depression, anxiety, impulsivity, and aggression are common.
- Disorders of consciousness: In severe cases, a person may be in a coma, vegetative state, or minimally conscious state.
- Increased risk of other conditions: TBI can increase the risk of developing degenerative brain diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) later in life.
A TBI is often a chronic condition requiring ongoing management. If negligence caused the injury, you may be entitled to compensation for both immediate and long-term care.
Prevention, Coping, and the Future of TBI Care
Preventing a traumatic brain injury is the best strategy. While not all accidents are avoidable, adopting simple safety habits can dramatically reduce the risk.
Key Prevention Strategies
Most traumatic brain injuries are preventable. Simple measures can make a significant difference:
- Wear seatbelts in vehicles and use appropriate car seats for children.
- Use helmets for activities like cycling, motorcycling, skateboarding, and contact sports.
- Fall-proof your home by installing handrails, using non-slip mats, improving lighting, and removing tripping hazards.
- Practice safe driving by never driving under the influence and avoiding distractions like texting.
- Follow workplace safety protocols, especially in high-risk industries like construction.
The CDC offers more detailed TBI prevention tips.
Coping Strategies for Individuals and Families
Living with a traumatic brain injury affects the entire family. The following strategies can help manage the challenges:
- Education: Understanding the injury helps set realistic expectations and reduces fear.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who share similar experiences provides comfort and practical advice. The Brain Injury Association of America is an excellent resource.
- Counseling: Therapy helps individuals and families process the emotional impact of TBI.
- Realistic Goals: Celebrate small steps in recovery and practice patience, as progress is often not linear.
- Stress Management: Use techniques like deep breathing or mindfulness to manage stress, as the brain is more sensitive after an injury.
- New Routines: Use calendars, reminders, and consistent organization to compensate for cognitive difficulties.
Latest Research and Advancements
The field of traumatic brain injury care is rapidly advancing, offering new hope for diagnosis and treatment.
- Biomarkers: Blood tests are being developed to detect brain-specific proteins, which could allow for faster diagnosis and better prediction of outcomes.
- Advanced Neuroimaging: Techniques like DTI and SWI can reveal microscopic damage that standard scans might miss.
- Neurostimulation: Non-invasive therapies like TMS and tDCS show promise in improving cognitive functions like memory and attention.
- Pharmacological Trials: Research continues to find drugs that can protect the brain after injury or promote healing.
- Personalized Rehabilitation: Therapies are becoming more customized to an individual’s specific cognitive challenges.
Large-scale research projects are accelerating progress. You can search for TBI clinical trials to learn about participating in new research. These advancements are improving our ability to help people recover and adapt after a TBI.
Frequently Asked Questions about Traumatic Brain Injury
Can a mild TBI have serious consequences?
Yes. The term “mild” can be misleading. A mild traumatic brain injury, or concussion, is still a serious injury that requires prompt medical attention. While many people recover fully, some develop post-concussion syndrome, where symptoms like headaches, dizziness, memory problems, and mood changes persist for months or even longer. These issues can significantly disrupt work, daily life, and relationships. Never underestimate any head injury.
How long does it take to recover from a TBI?
There is no single timeline for recovery from a traumatic brain injury. It varies based on the injury’s severity, the person’s age and overall health, and the quality of rehabilitation. Many people with mild TBIs recover within a few weeks to months. However, moderate to severe injuries often require months or years of rehabilitation, and some individuals may need lifelong care. Recovery is often a long process with ups and downs, requiring patience.
What is the difference between a TBI and an acquired brain injury (ABI)?
An acquired brain injury (ABI) is any brain injury that occurs after birth. A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a specific type of ABI caused by an external traumatic force, such as a blow to the head from a fall, car accident, or assault. Other types of ABIs that are not TBIs include brain damage from strokes, infections, or lack of oxygen. In short, all TBIs are ABIs, but not all ABIs are TBIs.
Navigating the Aftermath and Seeking Justice
Recovering from a traumatic brain injury is a long journey filled with medical appointments, emotional challenges, and financial strain. It affects not only the injured person but their entire family. No one should have to face this overwhelming reality alone.
If your injury was caused by someone else’s negligence—such as a careless driver, a negligent property owner, or an unsafe work environment—you have legal rights. You may be entitled to compensation for your medical bills, lost income, rehabilitation costs, and the profound impact on your quality of life.
At Adam Krolikowski Law Firm, we have over 25 years of experience representing people with injuries, including severe head trauma. We handle the complex cases that others may not, providing the legal guidance and compassionate support you need to rebuild your life.
If you are ready to explore your legal options, we are here to listen. Visit our personal injury lawyer page to learn how we can help guide you through the legal process. Your recovery and your justice are our priority.
Contact Us
Practice Areas
Recent Articles
- « Previous
- 1
- 2
- 3
- Next »

